Contents
Summary
Three higher education institutions demonstrate how strategic planning in higher education succeeds when it is agile, data-driven, and outcomes-focused. Their approaches show how responsive planning, measurable goals, and modern frameworks turn strategy into real institutional impact.
- Flexible plans outperform rigid, long-term strategies
- Data enables smarter decisions and continuous improvement
- Modern planning aligns strategy with real-world change
Higher education today operates in an entirely different cultural, political, and even economic environment than it did ten years ago. The emphasis on accessibility and equity has grown hugely, as institutions strive to serve increasingly diverse student populations. Online learning has moved from a niche offering to a cornerstone of educational delivery, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic. And, fitting with the trend we have seen in government, there has also been a sharp decline in public trust in higher education with questions about return on investment (ROI) and the value of a degree gaining prominence.
Leadership turnover has also accelerated. All levels and departments of higher education are impacted, with some statistics showing that presidents, provosts, and deans are leaving their roles at a 23.5% rate.
So, given all these fluctuations and realities in the higher education landscape, how can we go about understanding what makes a strategic plan worthwhile? What makes one work?
In other words, what makes a higher education strategic plan more than just the dusty document that sits on the shelf, into something that actually guides change?
We took a look at some of our highest performing and most forward-thinking higher education customers to learn more. They share in common the following three features:
- They are responsive and proactive (not reactive) to setbacks
- They use data to help resource and guide actions, especially around more challenging, abstract values, such as “belonging.”
- They are unafraid of change, embracing modern and innovative practices in improving their strategic planning and performance management processes.
Here are three examples of strategic plans in higher education that are innovative, agile, and realistically scoped for the kind of unique demands universities and colleges face. (Also, why we love them, and what you can learn from them!)
1. Agile and Proactive Strategic Planning Processes
We’ve outlined some of the challenges that universities and colleges face when it comes to implementing plans. As is the case with many areas of the public sector, higher education faces a lot of volatility.
If a strategic plan is not capable of balancing the tightrope between being dynamic and responsive, long-term plans risk losing relevance in a landscape where both leadership and the student demographic are in constant flux.
It can happen where leadership teams invest one to three years crafting a strategic plan, spend another year or two enacting it, only to be succeeded by new leadership that restarts the entire process. This recurring cycle disrupts continuity and dilutes the core purpose of strategic planning.
Higher education requires a flexible planning framework that maintains stability and momentum, regardless of leadership changes.
In our Volatile, Uncertain, Complex and Ambiguous (VUCA) world, the need for strategic planning has never been greater—but not in the traditional sense. A static, rigid strategic plan, set in stone for five or ten years, is ill-suited to a world that changes by the semester.
Strategic Plan Example 1: Catawba College, North Carolina
Catawba College is in the second year of its strategic plan. Their “A College of Our Own” strategic plan provides a detailed breakdown of their priorities, which include various enrollment tactics and KPIs. They demonstrate a strong commitment to strategic planning with their “A College of Our Own” initiative. Key highlights include:
- Clear focus: The plan outlines nine core annual priorities supported by 35 annual goals, providing a clear direction for the institution.
- Data-driven approach: Tracking progress through 490 linked activities and a dedicated “Strategic Plan Priority Scorecard” allows for data-driven analysis and adjustments.
- Emphasis on people: The “Our Investment in People” aim emphasizes a strong focus on student, faculty, and staff well-being, professional development, and equity.
- Continuous improvement: Acknowledgment of roadblocks such as limited IT resources and staff bandwidth demonstrates a realistic understanding of challenges and a commitment to finding solutions.
What we really love about Catawba’s planning process is how they identify, discuss, and create plans around potential roadblocks and disruptions. A successful strategic plan must be realistic and adaptable. Acknowledging potential (and existing) roadblocks is vital because:
- It anticipates challenges: Identifying potential obstacles allows for proactive planning and mitigation strategies. This prevents unexpected setbacks and maintains momentum towards achieving goals.
- It builds resilience: By acknowledging potential challenges, the institution fosters a culture of resilience and adaptability within its community.
- It improves decision-making: Recognizing roadblocks informs decision-making processes, allowing for the selection of more effective strategies and the allocation of resources more efficiently.
- It presents an opportunity for improved communication: Openly discussing challenges fosters transparency and builds trust.
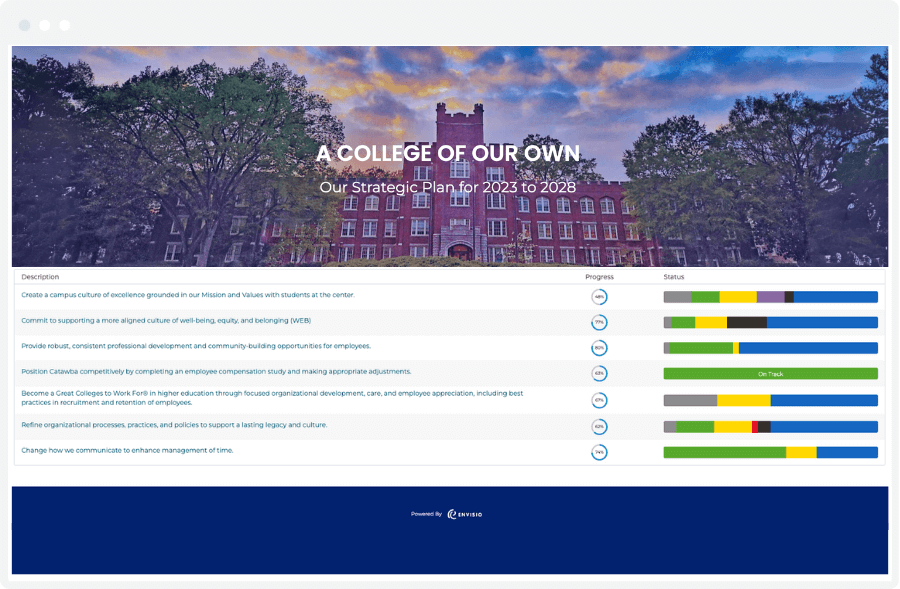
By proactively addressing potential roadblocks, Catawba College demonstrates a robust and adaptable approach to strategic planning, increasing the likelihood of achieving its long-term goals. And achieving goals and outcomes is what we want to see!

2. Data-driven Strategic Plans
Incorporating data into higher ed strategic planning not only helps institutions understand where challenges exist but also drives continuous improvement by enabling decision-making based on real-time insights. With this data-driven approach, higher education institutions can also turn their commitment to more challenging concepts, such as “trust” or “belonging,” into meaningful action items.
Equity, diversity, and inclusion (EDI) related initiatives have become critical priorities in higher education, and is an excellent area to utilize data-driven insights.
Institutions face a rapidly evolving landscape shaped by the pandemic, economic challenges, heightened awareness of racial injustice, and shifting societal expectations.
Another notable element related to higher education and its relationship to equity is, in particular, Generation Z students. Data shows the generation of current college goers demand accountability, transparency, and real action from their colleges and universities, making it essential for institutions to craft EDI strategic plans that deliver measurable results.
So in 2025, a higher education strategic plan ideally does more than merely acknowledge the importance of diversity; it actively integrates inclusiveness into the institution’s operations and culture. Ways of doing this include:
- Actionable steps: Ensuring there are actionable steps tied to each strategic objective, ideally “SMART” goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Resourced, and Time-Bound).
- Communication: Communicating transparently and frequently, for instance through a public dashboard that can clearly label initiatives as “complete,” “in progress,” “disrupted,” or “not yet implemented” to signal continuous engagement and prioritize areas needing further focus.
- Data-driven: Data helps institutions identify where gaps exist and where progress is being made, which is why it’s so useful for any equity-centered strategic plan. It also allows for a more objective approach to measuring success and adjusting strategies in real-time based on what’s working.
Strategic Plan Example 2: Green River College, NC
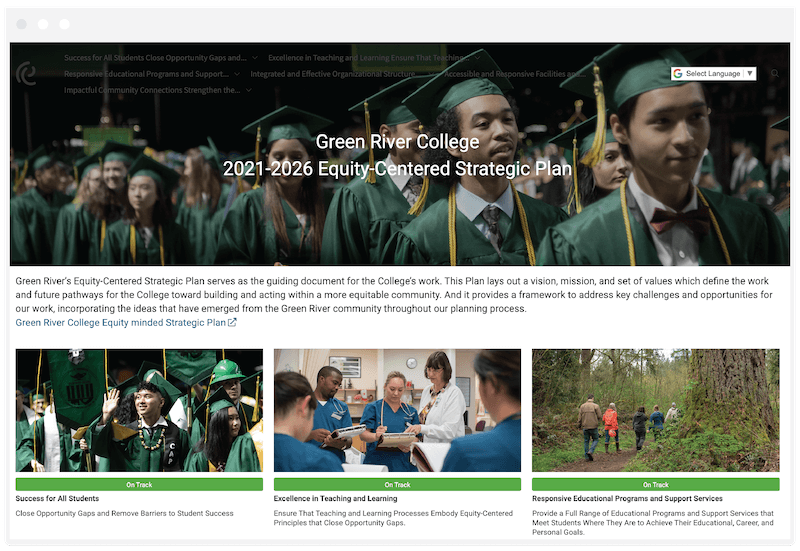
Green River College’s 2021-2026 Equity Strategic Plan serves as a model of excellence in equity-centered strategic planning in higher education.
And the data piece?
The College developed it after completing an environmental scan, after which they found several indicators that needed improvement. For instance, they found that student retention and success rates at Green River varied by ethnicity, being lower amongst historically marginalized and racialized groups. They also found that there could be improvement with further linking programming with local community needs.
Here’s what we love about it as a higher education strategic plan:
- Comprehensive vision and vocabulary: The plan outlines a clear institutional commitment to equity, defining key terms like “equity,” “inclusion,” and “justice.” This shared understanding aligns everyone around a unified mission.
- Actionable goals: Green River College emphasizes SMART goals, detailing specific actions such as increasing the recruitment and retention of underrepresented students and faculty, implementing bias training programs, and expanding community partnerships.
- Transparent communication: Green River College’s commitment to transparency is evident through its public dashboard, which provides updates on key initiatives and metrics, and acknowledges areas for improvement. This openness fosters trust and engagement within the campus community.
3. Modern and Outcomes-driven Strategic Planning Approaches
Higher education institutions need a modernized approach to strategic planning, one that prioritizes actionable, agile strategies over static plans. It’s both inspiring and just straight up better planning to focus on strategies that drive institutional transformation, align with overarching priorities, and inspire staff, as well as prospective and current students and researchers.
Strategic Plan Example 3: The Southern Virginia Higher Education Center (SVHEC)
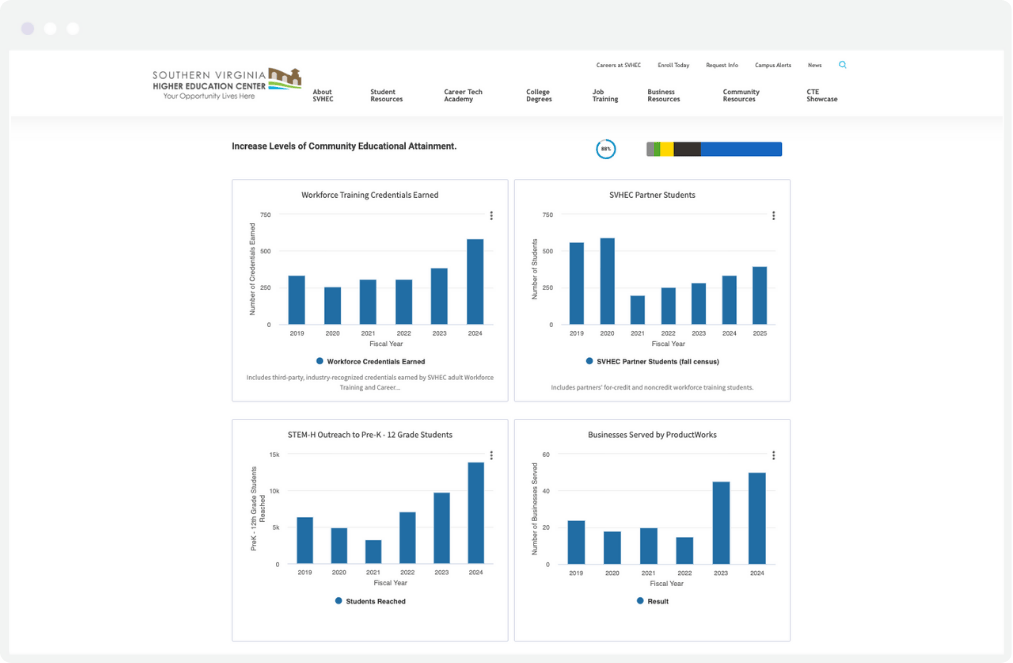
Faced with the challenge of revitalizing a region impacted by economic decline, SVHEC, led by Dr. Betty Adams and her team, adopted strategic planning and performance management practices that are both visionary and results-driven.
Key reasons why SVHEC’s strategic plan and implementation process is a standout example of higher education strategic planning:
- Mission-driven strategy: SVHEC’s mission to enhance the economic potential of Southern Virginia guides its efforts. By offering technical training, degree programs, and workforce readiness initiatives, the center addresses local needs and encourages residents to remain in the region.
- Collaborative model: Operating as a state-designated higher education center, SVHEC partners with community colleges, public schools, and employers to deliver in-demand training and credentials, creating pathways for high school students and adults alike.
- Community impact: The center has contributed to reversing population decline in Halifax County and increasing local workforce participation, demonstrating tangible success in addressing regional economic challenges.
- Flexibility and responsiveness: SVHEC adapts quickly to community needs, as evidenced by initiatives like the IT Academy, Healthcare Training Hub, and Career Tech Academy.
By leveraging strategic planning, fostering partnerships, and embracing technology, SVHEC has transformed into a model of resilience and progress, proving that higher education institutions can lead economic revitalization and community growth.
Read more about SVHEC’s journey to strategic success here.
Strategic Planning Matters in Higher Education
The examples from Catawba College, Green River College, and the Southern Virginia Higher Education Center highlight how dynamic, data driven, and results-oriented plans can make a significant impact on the implementation of those plans.
As you reflect on the future of your own institution, take note of the importance of crafting plans that are flexible, driven by data, and designed to address the unique challenges of today’s educational landscape. A truly successful strategic plan doesn’t sit idle; it evolves, engages, and delivers real outcomes.
Next Steps for Your Strategic Plan
If you’re in the process of creating or refining your strategic plan, let’s talk. Learn new ways to set up your plan for success – from staff alignment to better visibility into progress. We work with higher education institutions across North America to help them implement strategy and drive outcomes.
Book a call and let’s get started.




